CST test
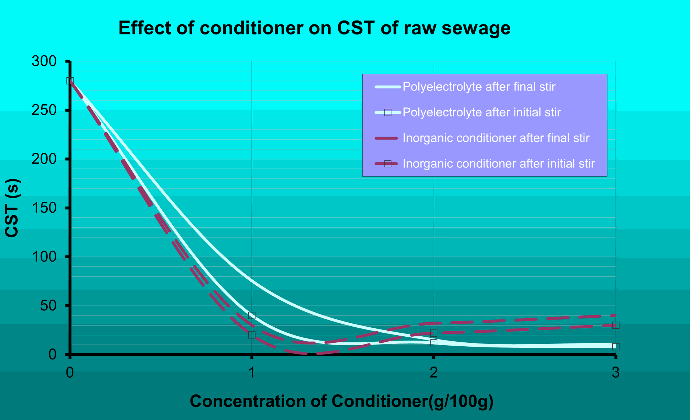
Capillary Suction Time (CST) has been established as a reliable method for assessing sludge filterability.
The equipment was originally developed for use with sewage sludge and it is for this reason that most quoted examples deal with sewage sludge, however the CST technique can be used on any colloidal aqueous suspension. In particular the petrochemical industry has developed the CST to assess bore hole sludge.
The method is simple and fast to use, and the results generated can be related to the Buchner funnel and American Petroleum Institute filtration procedures.
Interpretation of the CST results
Generally, the lower the CST the better the sludge filterability. As target figures, the following CSTs are considered acceptable for a typical sludge of 5% solids concentration, using the 1.8cm funnel:
- Filter-belt press Less than 10 but increasing with shear
- Filter press 15 to 20 but stable with shear
- Centrifuge 15 or less but very stable with shear
Flocculant dosing
A typical use of the CST is to determine ideal dosing levels to ensure good dewaterability without introducing excessive flocculant. Not can that be costly but it can reduce plant efficiency by clogging filter media.